The H-1B visa program has long been a contentious issue in the United States, with proponents arguing that it is essential for attracting highly skilled foreign workers and contributing to the nation’s economic growth. Critics, on the other hand, contend that it depresses wages for American workers and leads to outsourcing of jobs.
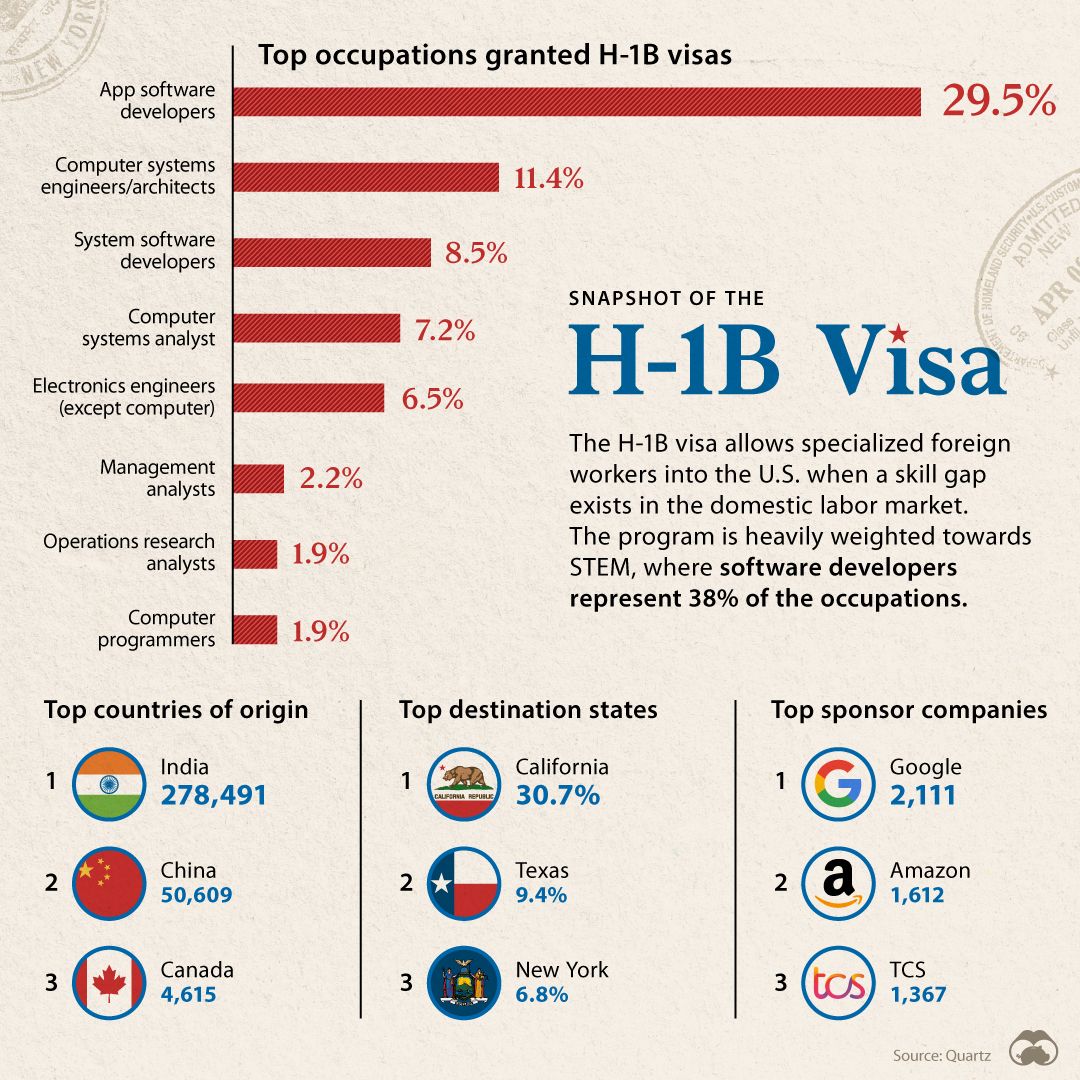
The H-1B visa is a non-immigrant visa that allows US companies to hire foreign workers in specialty occupations that require theoretical or technical expertise in specialized fields, such as computer science, engineering, and medicine. The program has an annual cap of 85,000 visas, with an additional 20,000 visas available for individuals with a master’s degree or higher from a US university.
H-1B visas are typically valid for three years, with the option of a one-time extension for an additional three years. During this period, visa holders are permitted to work only for the petitioning employer and must be paid the prevailing wage for their profession.
Republican lawmakers have expressed growing concerns about the H-1B program, arguing that it has been abused by companies to replace American workers with cheaper foreign labor. They point to data showing that the number of H-1B visas issued has increased steadily in recent years, reaching a record high of over 400,000 in 2022.
Republicans also argue that the program is unfair to American workers, who must compete with foreign workers for jobs and face downward pressure on wages. They contend that companies should prioritize hiring American citizens and permanent residents before seeking to bring in foreign workers on H-1B visas.
Industry leaders, particularly in the technology and healthcare sectors, have strongly defended the H-1B program. They argue that it is essential for attracting and retaining the best and brightest talent from around the world, which is crucial for innovation and economic growth.
Companies claim that many of the jobs filled by H-1B visa holders are highly specialized and require skills that are not readily available in the domestic workforce. They also argue that H-1B workers often contribute to job creation and stimulate the economy by starting their own businesses or investing in US companies.
Data on the impact of H-1B visas is mixed. Studies have shown that the program can lead to increased innovation and economic growth in the short term. However, there is also evidence that it can have negative consequences for American workers, particularly in certain occupations.
A study by the National Bureau of Economic Research found that a 10% increase in H-1B visas in a local labor market leads to a 0.2% decline in wages for native-born workers with similar skills. The study also found that H-1B visas can lead to a reduction in the number of patents filed by American inventors.
In response to these concerns, Republican lawmakers have introduced several legislative proposals aimed at reforming the H-1B program. These proposals include:
- Increasing the prevailing wage requirement for H-1B workers
- Limiting the number of H-1B visas that can be issued to each company
- Requiring companies to demonstrate that they have made a good-faith effort to hire American workers before seeking H-1B workers
These proposals have met with resistance from industry groups and some Democrats, who argue that they would make it more difficult for companies to hire the skilled workers they need to compete in the global economy.
The debate over H-1B visas is complex and there are valid arguments on both sides. The program has the potential to benefit both the US economy and American workers, but it is essential to ensure that it is not abused and that the interests of American workers are protected.
Ultimately, the best solution will likely involve a delicate balance that addresses the concerns of both industries and workers. This may require a combination of measures, such as increasing the prevailing wage requirement, limiting the number of visas issued to each company, and providing more support for American workers in training and education programs.
By carefully examining the evidence and engaging in thoughtful debate, US policymakers can work towards a reformed H-1B program that maximizes its benefits while mitigating its potential negative consequences.

